Raspberry Pi Measurement of voltage and current at the GPIO output with high level under load
If you connect a high-level GPIO output to a Raspberry Pi, then you expect a voltage of 3.3 volts. Unfortunately, a GPIO output changes its voltage and current behavior under load.
How exactly can be determined with a series of measurements.
Measurement series
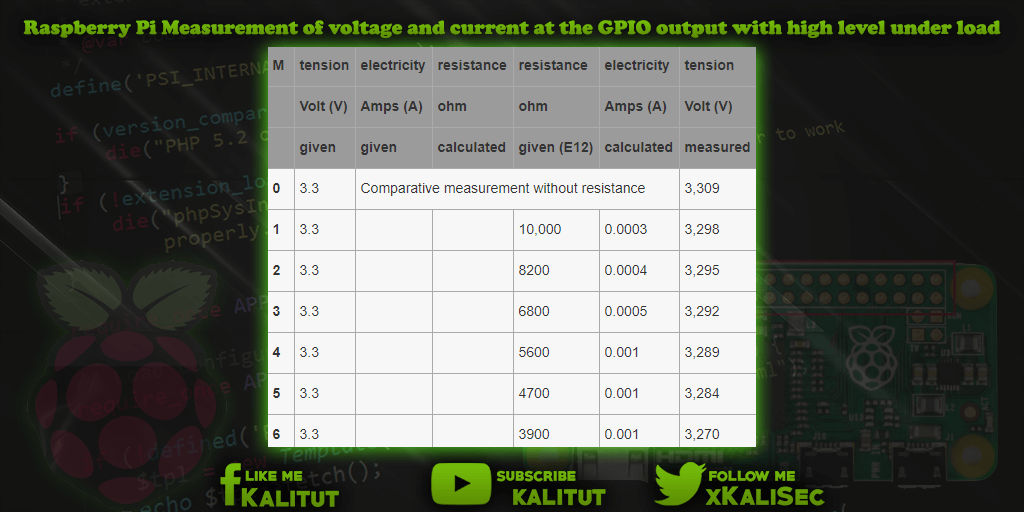
| M | tension | electricity | resistance | resistance | electricity | tension | electricity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volt (V) | Amps (A) | ohm | ohm | Amps (A) | Volt (V) | Amps (A) | |
| given | given | calculated | given (E12) | calculated | measured | measured | |
| 0 | 3.3 | Comparative measurement without resistance | 3,309 | deleted | |||
| 1 | 3.3 | 10,000 | 0.0003 | 3,298 | 0.00033 | ||
| 2 | 3.3 | 8200 | 0.0004 | 3,295 | 0.00041 | ||
| 3 | 3.3 | 6800 | 0.0005 | 3,292 | 0.00049 | ||
| 4 | 3.3 | 5600 | 0.001 | 3,289 | 0.00058 | ||
| 5 | 3.3 | 4700 | 0.001 | 3,284 | 0.00071 | ||
| 6 | 3.3 | 3900 | 0.001 | 3,270 | 0.00086 | ||
| 7 | 3.3 | 0.001 | 3300 | 3300 | 0.001 | 3,264 | 0.00101 |
| 8 | 3.3 | 2700 | 0.001 | 3,254 | 0.00122 | ||
| 9 | 3.3 | 2200 | 0,002 | 3,242 | 0.00149 | ||
| 10 | 3.3 | 1800 | 0,002 | 3,228 | 0.00182 | ||
| 3.3 | 0,002 | 1650 | |||||
| 11 | 3.3 | 1500 | 0,002 | 3,210 | 0.00215 | ||
| 12 | 3.3 | 1200 | 0,003 | 3,185 | 0.00268 | ||
| 3.3 | 0,003 | 1100 | |||||
| 13 | 3.3 | 1000 | 0,003 | 3,167 | 0.00317 | ||
| 14 | 3.3 | 0,004 | 825 | 820 | 0,004 | 3,128 | 0.00393 |
| 15 | 3.3 | 680 | 0.005 | 3,091 | 0.00472 | ||
| 3.3 | 0.005 | 660 | |||||
| 16 | 3.3 | 0,006 | 550 | 560 | 0,006 | 3,053 | 0.00556 |
| 17 | 3.3 | 0,007 | 471 | 470 | 0,007 | 3,001 | 0.00662 |
| 3.3 | 0,008 | 413 | |||||
| 18 | 3.3 | 390 | 0,008 | 2,945 | 0.00779 | ||
| 3.3 | 0.009 | 367 | |||||
| 19 | 3.3 | 0,010 | 330 | 330 | 0,010 | 2,883 | 0.00910 |
| 3.3 | 0.011 | 300 | |||||
| 20 | 3.3 | 0,012 | 275 | 270 | 0,012 | 2,793 | 0.01100 |
| 3.3 | 0,013 | 254 | |||||
| 3.3 | 0,014 | 236 | |||||
| 21 | 3.3 | 0,015 | 220 | 220 | 0,015 | 2,709 | 0.01241 |
| 3.3 | 0.016 | 206 | |||||
| 22 | 3.3 | 180 | 0,018 | 2,582 | 0.01527 | ||
| 23 | 3.3 | 150 | 0,022 | 2,472 | 0.01633 | ||
| 24 | 3.3 | 120 | 0.028 | 2,313 | 0.01929 | ||
| 25 | 3.3 | 100 | 0.033 | 2,166 | 0.02289 |
||
The table consists of a total of 3 parts. The first part consists of the voltage of 3.3 volts (column 2) applied to the GPIO output (high) and a current from 0.001 A to 0.016 A (column 3). In order for the given current to be set below the specified voltage, a corresponding resistor must be used for this purpose, which was calculated for this purpose (column 4).
The second part of the table is that the calculated resistance values are not real resistances, but real resistances with other values have to be used. In this case from the E12 series (column 5). In some cases, there are overlaps with the calculated resistance values (between columns 4 and 5). Since a given current is set at a specified voltage at a given voltage, it was calculated (column 6). This current is what would be expected at the specified voltage of 3.3 volts.
The third part of the table deals with the actual measurement of voltage and current (columns 7 and 8). Here, first the voltage at the GPIO output (high level) was measured (column 7) to see if there are really 3.3 volts at the resistor. The current measurement was then performed (column 8) to see if the calculated current actually flows through the resistor.
The measurement 0 was made to check whether there really is a high level at the GPIO output and how high the high level is to be expected. The current measurement is omitted here, because there is no closed circuit here. Subsequently, the measurement was carried out 1 to 25. Once each for the GPIO output voltage and the GPIO output current.
Observation and evaluation of the measurements
- As the resistance decreases, the output voltage at the GPIO decreases.
- As the resistance decreases, the output current at the GPIO increases.
- As the output current increases, the output voltage at the GPIO drops.
While a stable voltage and current ratio is set up until measurement 22, from measurement 23 the measured value can only be read off the meter with difficulty. From 0.016 A or 16 mA, a GPIO output starts to float. The values for voltage and current fluctuate.
Findings and conclusion
The measurements show that a GPIO output under load has a lower output voltage than expected. When a current flows, the voltage drops. However, the actual output current remains behind the calculated current.
A GPIO output is a digital output that should not be loaded because the output voltage drops due to the output current. That is, the subsequent wiring must also be able to detect a voltage below 3.3 volts as a high level. That is to be tested. Or you have to make sure that the GPIO output is not loaded.
Basically, the output current must be limited. It would be better, however, to understand the GPIO output as a digital output, which you cannot remove power, but may only pick up the voltage level. A subsequent switch stage should be voltage and not current controlled. So a FET instead of a bipolar transistor.

Leave a Reply