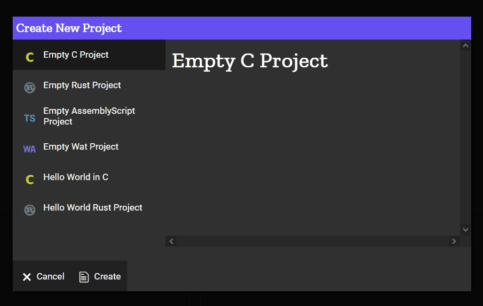
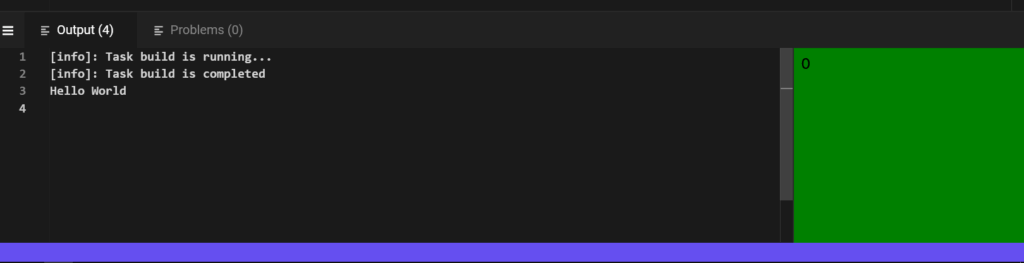
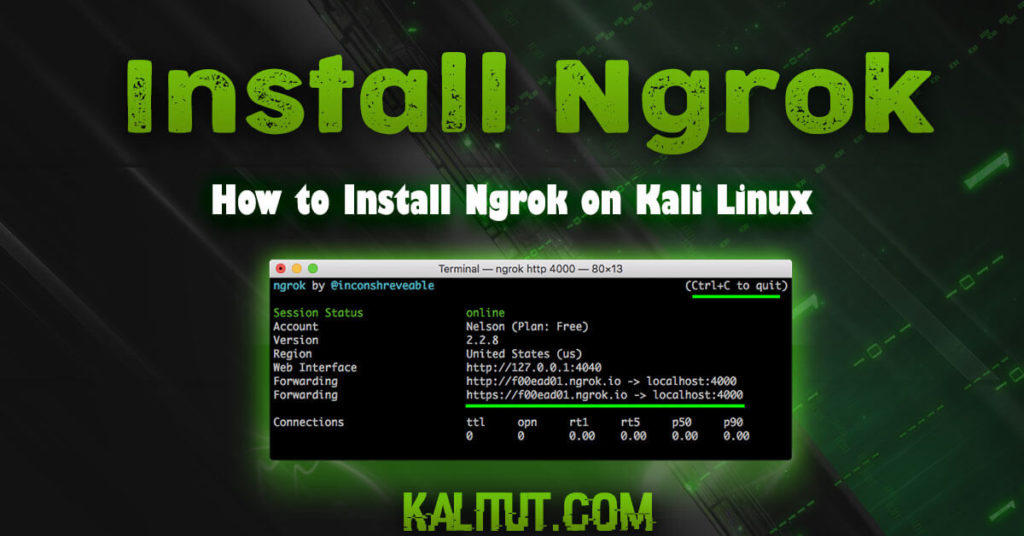
This is the ultimate PowerShell tutorial . Here you will learn everything about console programs and commands from PowerShell, CMD and Bash.

In this tutorial (almost) everything works without a graphical user interface .
[Read more…] about PowerShell Tutorial – GUIDE introduction with basics