Kali Linux distribution has officially followed the Swiss hacker knife BackTrack. Kali Linux is – just like BackTrack – a Linux especially for those who are interested in penetration testing, the (un) security of systems or want to recover data that seems to have disappeared. And yet, a lot is different. Offensive Security officers have risked a fresh start, leaving behind legacies.

Kali Linux thoroughly cleans up its predecessor’s historic toolkit and presents users with a well-stocked set of specialized tools in categories appropriate to their intended use. “We reviewed every tool included in BackTrack, eliminating many programs that either did not work or whose functions overlapped with other tools “, write the responsible persons in the wiki. If you had to know what to look for at BackTrack, the new sorting would rather invite you to browse.
The most important programs can be found in the category “Top 10 Security Tools”; including classics such as the password cracker John the Ripper, the network sniffer Wireshark, the web analytics proxy Burp, the port scanner NMAP and the exploit framework Metasploit. Through the re-sorting, you can easily find the rest of the more than 300 special tools.
In addition to the usual 32- and 64-bit versions, Offensive Security also offers an ARM edition, which also runs on platforms that you would not call a classic PC, such as the Mini-Recher Raspberry Pi or a SainSmart SS808 in stick format. Also on the Chromebooks from Samsung is the distribution. According to the responsible persons, Kali supports as many WLAN interfaces as possible “. It is based on Debian with the kernel version 3.7 and should already contain important patches for the introduction of data packets into WLAN networks.
Kali Linux Tools
information gathering
If you want to analyze or attack a system, you should first know its environment and collect some information. Below we would like to briefly introduce some tools:
Nmap
This tool is a scanner with which you can examine firewalls for open ports. In addition, Nmap may try to detect the OS’s operating system.
Wireshark
Wireshark is a network traffic analysis tool, facilitated by color tags and filters. Insofar as data is sent via unencrypted channels in the network, even user names and passwords can be read in plain text.
Vulnerability Analysis
Everyone who runs their own IT systems, especially in the area of servers and networks, should periodically analyze their infrastructure for possible leaks. To bring Kali Linux, among others, the two tools OpenVAS and Greenbone Security Assistant with.
Web Applications
In the field of web applications, there are, among other things, tools for checking content management systems (CMS) for weaknesses. My personal favorite is here WPScan because now every fourth website on WordPress running. Another representative in this area would joomscan for the CMS Joomla.
Database Assessment
Also, databases are no problem for Kali Linux, because there are tools like jSQL and SQLdict provided.
Password attacks
If you do not want to penetrate vulnerabilities in a system, then you have the opportunity to use weak passwords to penetrate the system. A popular tool for cracking passwords is John the Ripper, which uses a brute force attack to crack the password, but this process can take a long time. This is where crunch comes in, as this tool can generate word lists. For the cracking of logins, the tool can THC-Hydra be used. This one has support for many different logins.
Wireless attacks
Also in the area of radio systems, Kali Linux offers a variety of tools with which you can crack systems. For the area of WLAN systems, there is Aircrack-ng, which makes it possible to carry out various attacks on WEP, WPA and WPA2. Another tool in this area is Reaver. It starts with the WPS standard but is not always reliable when cracking. In all of the other wireless areas can with RTLSDR work, but this presupposes the jewelige antenna for transmitting and receiving signals. usb wifi adapter monitor mode
Reverse engineering
Sometimes you want to analyze unknown software for their functionality, for example, to uncover vulnerabilities or to analyze the behavior of malware. For this case, Kali Linux offers among other tools to investigate APKs.
Exploitation tools
Again and again, you hear about exploits for different systems, but mostly you do not know how to use them for an attack. At this point, the Metasploit framework, which is able to analyze several hosts simultaneously and attack with different exploits, supports this. However, since this tool is operated via the console, it is not suitable for everyone. Help is provided by Armitage, a graphical interface for the Metasploit framework.
Sniffing and spoofing
Sniffing and spoofing are important methods in the field of IT security in order to obtain targeted data in the network. Two representatives of these tools category are SniffJoke and Wifi Honey.
Post exploitation tools
Once you have managed to gain access to a system via an exploit, it should also be well established. Post exploitation tools, such dns2tcp and Web shells, offer themselves for excellent and are also an integral part of Kali Linux.
forensic science
No matter how secure the system may be, it can still lead to suspicious incidents. In such cases, one enters the field of IT forensics. For the acquisition, analysis and evaluation of digital traces is Kali Linux tools like iPhone Backup Analyzer and pdf-parser ready.
Reporting
At the end, there is always the report, in which the findings of all analyzes are recorded. Even at this point provides Kali Linux support tools such as Case File and MagicTree.
Quick start with Kali Linux
More than 300 tools for targeted penetration testing are provided by the special Kali Linux . We introduce our favorites and show how to use them.
If you want to tap a network for its security or analyze the traffic of an app, you quickly land on Linux. The special distribution Kali Linux comes with a bulging tool case that makes the hearts of hackers and pen testers beat faster.
As a substructure for Kali Linux Debian Wheezy is used, which is content with 512 MB of RAM and 10 GB of disk space. Alternatively, you can even start it on a Raspberry Pi. The “Applications, Kali Linux” menu takes you to the treasury, which contains over 300 tools. We have assembled prominent pentesting tools as well as rarely noticed beads that invite you to experiment.
Needless to say, you must always make sure that you do not violate the laws of your country. That means in case of doubt, that you only use the tools for your own services – or at least with the explicit consent of the operator.
The developer Offensive Security offers Kali for 32-, 64-bit and ARM systems for download. Although the ISO images start as a live system, if you like it you can also initiate an installation. There is also a pre-built VMware machine. Anyone who decides on the live system or the virtual machine, the first official act probably wants to adjust the default US keyboard layout in the system settings in the system settings to the local conditions.
You will find the wheel via “Applications, System Tools, Preferences, System Settings, Region and Language”. There you can also change the system language. Note that these changes to the live system will not survive the next boot. If you install Kali Linux, however, you can make these settings via the setup wizard. With the commands and bring the system up to date after commissioning.
apt-get update apt-get upgrade
How to install kali linux on virtualbox
How to update kali linux
How to setup kali linux on usb
Fix kali linux sources.list
Scan and redirect
Network Scan
Although Kali boots with a graphical interface, the pivotal point is usually the console. Among other things, it can be reached via the black and white rectangle, at the top left of the status bar. For many operations, you need a network. The command shows whether and which of the existing network interfaces has been provided with an IP address via DHCP.
ifconfig -a
If necessary, assign an IP manually as follows:
ifconfig eth0 192.168.0.2 netmask 255.255.255.0
The first parameter corresponds to the name of the interface. This is followed by the desired IP address, the string “netmask” and the network mask. Kali Linux supports numerous wireless LAN adapters. The best way to configure it is to use the Network Manager, which announces its presence in the upper-right corner of the screen with an icon showing two computer
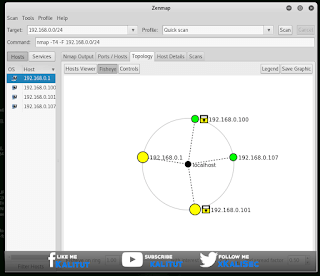
This Kali Linux is on the net – but what else? With the network scanner, Nmap can be found out very quickly. Launch its graphical user interface by Zenmap tapping the console. The goal is the local network.
If the system has the IP address 192.168.0.2, enter 192.168.0.0/24, which causes Nmap to scan the address block 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.0.255.
As a profile, select the superficial “Quick scan” for the test run. Now press the scan button, whereupon a list of the answering network participants is established in the left window area. The “Ports/Hosts” tab tells you which ports the clients are responding to.
Man in the middle
If you encounter a network scan on clients that can not really be assigned, a targeted analysis of the traffic sometimes provides valuable information. In the usual network configurations, however, foreign traffic does not pass the analysis system, which is why you need to set up a rerouting through so-called arp spoofing. That sounds more complicated than it is.
First, instruct Kali Linux to forward the client’s impulsive data packets to their actual destination, the router:
echo 1/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Then manipulate with arpspoof the ARP table of the victim. This specifies which IP address belongs to which MAC address. Use the following command to convince the client to send packets destined for the IP address of the router to the MAC address of the Kali machine:
arpspoof -i eth0 -r -t 192.168.0.5 192.168.0.1
eth0denotes the network interface used and -r causes the traffic to be redirected in both directions. So you also receive the packets that the router sends to the client. The parameter -t(like Target) is followed by the IP address of the victim (in our example 192.168.0.5) and last but not least you specify the IP of the router.
With Kali Linux you are now in the powerful position of “Man in the Middle” – between the client to be analyzed and the router. Now is the time to take tcpdumpa look at the traffic passed through the tool :
tcpdump -i eth0 -A host 192.168.0.5
If the client is currently active, its traffic is now rushing through the console. You can also understand this effect with the graphical tcpdump equivalent Wireshark.
Since almost everything speaks in the meantime with the Internet, it is important to filter the flood of data in a meaningful way. For example, to display only traffic on HTTP port 80, hang it and port 80on the command. In turn, one would only display packets containing a particular string. | grep Suchbegriff
For many obvious filtering tasks, Kali Linux brings specialized tools. For example, it extracts url snarf only HTTP requests from the data stream. Visually impressive driftnet: After the start, the images transmitted in the network scroll over the screen. Anyone who still operates an inadequately protected Wi-Fi is probably convinced of the seriousness of the situation at the latest when in-company or holiday memories flicker across a foreign screen in real time. If that’s not enough, you can go with it sniff go one step further: The snooping program detects access data that is transmitted, for example, when logging on to websites, when sending mail or when establishing a connection with an FTP server.
Of course, these tools are limited. Once encryption is used, the contents of the data packets, if any, can only be learned by a deep grip on the bag of tricks.
SSl Strip
Decryption tricks If you want to evaluate the contents of encrypted connections, you do not necessarily have to crack the encryption – you can also speculate on the carelessness of the user: The tool sslstrip replaces as a forced proxy all references to https:// addresses through http://. In the case of Chrome and Firefox, however, this only works reliably with older browser versions. The current ones evaluate the HSTS header, which allows a server to tell the browser to communicate exclusively over HTTPS. The Internet Explorer in the development of this article current version 11 is still on sslstrip purely.
Encryption is only used between sslstrip and the service. This is necessary because many services can now only be accessed via HTTPS. However, sslstrip is not quite as trivial as the previous helpers: In order for the data traffic to arrive at the tool, you must iptables redirect the traffic with the network filter. It also requires an unencrypted entry point, such as automatic redirection from http://paypal.com to https://paypal.com. If the user purposefully steers the HTTPS address, he can sslstrip not check in.
If, for example, you want to examine the crypto traffic of a smartphone app, you have to choose a universal approach. The forced proxy ssl sniff serves the data packets as opposed to being sslstrip encrypted. So that the tool can read the plaintext, it plays the target server to the victim. For this, ssl sniff issues a matching certificate with the name of the server with its own CA. Because the application on the client does not trust this CA, it displays a warning or rejects the encrypted connection. To prevent this, the client must import the CA certificate. That requires physical access – but that’s not a hurdle if the app being analyzed is running on your own smartphone anyway.
For convenient analysis and manipulation of HTTP (S) requests, Kali brings a number of web analysis proxies. The most prominent members of this genus are called Burp Suite, OWASP’s Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP) and mitmproxy. The programs provide their services on the local network by default on port 8080. Conducted connections can not only be viewed, but also intercepted interactively, and then sent with manipulated values to their actual destination. For example, developers can selectively feed traffic between the browser and the web application with unexpected content to detect potential security vulnerabilities. Burp and Zap provide extensive user interfaces, mitmproxy running on the console. Which candidate one attacks, is ultimately a matter of taste.
WiFi Tools
If you set up a router, you will be spoiled for choice of frequency. In densely populated areas, it makes sense to set a channel where there is little traffic. Kali knows many tools for analyzing WLAN airspace. Before you start, you should check whether the connected WLAN interface has been recognized by the system and what it is called. So that the interface also passes through WLAN packets intended for other MAC addresses, you must activate the so-called Monitor Mode: iwconfig
airmon-ng start wlan0
If this succeeds, you will find iwconfiga new wireless interface called mon0. Then tap to get a detailed overview of the surrounding Wi-Fi networks. You answer the pop-up dialogs with “OK”, “Yes” and “Start”. If kismet asks if you want to add an interface, you affirm this and enter the previously determined monitor interface name under “Intf”. Use the Tab key to “Add” and press “Close Console Window” in the next dialog in the same way. kismet
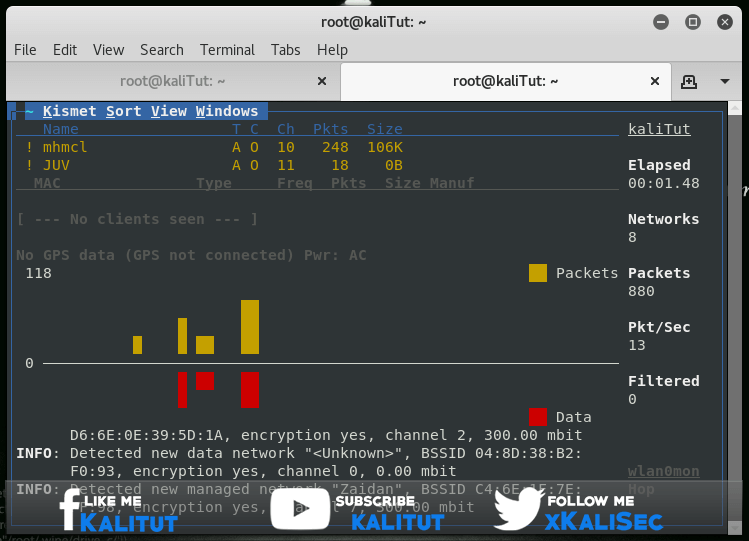
kismet Gradually, a comprehensive picture of the surrounding WiFi networks is emerging. The monitor mode allows you to check the activities of all WLANs and to determine how many clients are connected and how many data packets are currently sent to them. Also, “hidden” networks appear in the list. If you would like to investigate a specific network, you should bind the interface to its channel via “Kismet, Config Channel …”. Otherwise, Kismet rattles off the wireless channels continuously in order.
For other WLAN experiments invite the other members of the family
aircrack-ng, which also airmon-ng belongs. You can feel it by entering and pressing the Tab key twice. For example, you can demonstrate with the credulity of most wireless LAN clients: The tool spans a virtual Wi-Fi hotspot of arbitrary name (SSID). If the SSID corresponds to the identifier of an unencrypted WLAN that one of the clients is aware of within wireless range, the latter attempts to establish a connection. air airbase-ng

If you want to get an idea of how vulnerable your Wi-Fi is, Kali also has tools for you. Many of them combine the Fern WIFI Cracker (the appropriate command is fern-wifi-cracker) under a graphical interface. According to the developers, it picks up both WEP Encryption and WPA / WPA2. While WEP is known to crack fast, one sometimes has to spend a lot of time with the two newer encryption standards. At sufficiently long and complex passwords Fern also bites his teeth. Faster then may lead to guessing the WPS pin to the destination, for which Fern uses the tool reaver.
Kali is not only getting closer to WiFi, but also to Bluetooth and NFC. In addition, you can use the included tools, for example, a cheap DVB-T stick in a so-called software defined radio (SDR) to convert, which searches on other frequencies for “life”. The appropriate tools can be found under “Applications, Kali Linux, Wireless Attacks”.
Forensics and attacks
Reconstruct Kali is not limited to investigating live communication, but also masters the forensic analysis of data carriers. No matter whether you inspect the disk of a virus-infected Windows computer or look for SD cards for lost-remembered vacation memories – Kali Linux brings the appropriate tools in the category “forensics”. In order not to unintentionally change the data medium to be dissected, one should first draw an image of it, which henceforth serves as a basis for work. With the self-explanatory Guymager, this is done with a few mouse clicks.
To analyze the image Kali brings, for example, the general purpose weapon Autopsy, which restores, among other things, long-deleted files, if they have not already been overwritten with new files. For rescuing deleted photos, there is a specialist called recover jpeg. If you want to get even deeper into the subject of forensics, you will find in the subfolder “RAM-Forensics” the tool Volatility, which uses a memory image to obtain detailed information about what was going on inside a computer at some point in time.
Simulated emergency
The special tools from the subfolder “Exploitation Tools” can, among other things, simulate virus attacks under real conditions. Anyone looking around should know what he is doing. The most powerful tool in this division is the Metasploit framework, which brings exploits to many programs. For example, it’s easy to demonstrate how easy it is to hijack a machine that does not have the most recent version of Java installed on it. With Armitage is also a kind of graphical interface included. If you just want to look around, you can search the exploit arsenal of Kali Linux with the command. The Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET) simulates, as the name implies, social engineering attacks, such as targeted phishing.
search sploit such begriff
Hardware Hacks
Kali Linux has a heart for microcomputers. On the one hand, it brings the Arduino developer environment, on the other hand, it also runs on many embedded devices. There are images for ARM devices such as the Samsung Galaxy Note 10.1, a Samsung Chromebook, HDMI sticks and the single-board computer Raspberry Pi. So you can assemble for small money an individual pentesting device, which is well through the sparing ARM architecture suitable for continuous operation. A Raspberry equipped with a standard USB WLAN stick, for example, results in a Wi-Fi honeypot, which you can even use with batteries or batteries. The imagination knows no bounds …

Leave a Reply