Many users do not even realize that by filling in the login and password when registering or authorizing on a closed Internet resource and pressing ENTER, this data can easily be intercepted. Very often they are transmitted over the network in a non-secure manner. Therefore, if the site on which you are trying to log in uses the HTTP protocol, it is very easy to capture this traffic, analyze it using Wireshark and then use special filters and programs to find and decode the password so how to capture passwords with wireshark.
The best place to intercept passwords is the core of the network, where all users’ traffic goes to closed resources (for example, mail) or in front of the router to access the Internet when registering with external resources. Adjust the mirror and we are ready to feel like a hacker.
How to capture traffic with wireshark
.
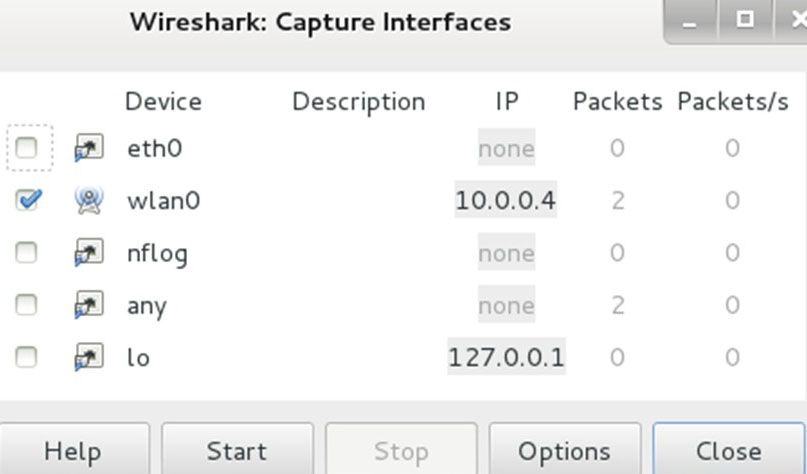
Sometimes for this purpose it is enough to select only the interface through which we plan to capture traffic, and click the Start button. In our case, do capture over the wireless network.
Traffic capture has begun.
Filtering captured POST traffic
We open the browser and try to log in to any resource using the login and password. Upon completion of the authorization process and the opening of the site, we stop capturing traffic in Wireshark. Next, open the protocol analyzer and see a large number of packets. It is at this stage that most IT professionals give up, because they do not know what to do next. But we know and we are interested in specific packages that contain POST data that is generated on our local machine when the form is filled on the screen and sent to the remote server when you click the “Login” or “Authorization” button in the browser.
Enter in the window a special filter to display captured packets: http. request. method == “ POST”
And we see instead of a thousand packages, only one with the data we are looking for.
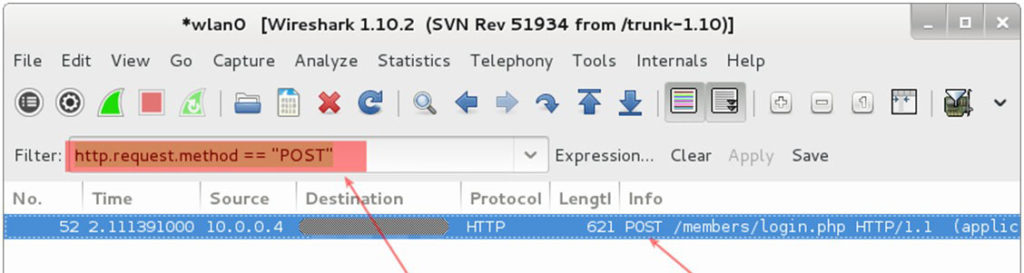
Find the username and password using Wireshark
Quick-click the right mouse button and select the Follow TCP Steam item from the menu.
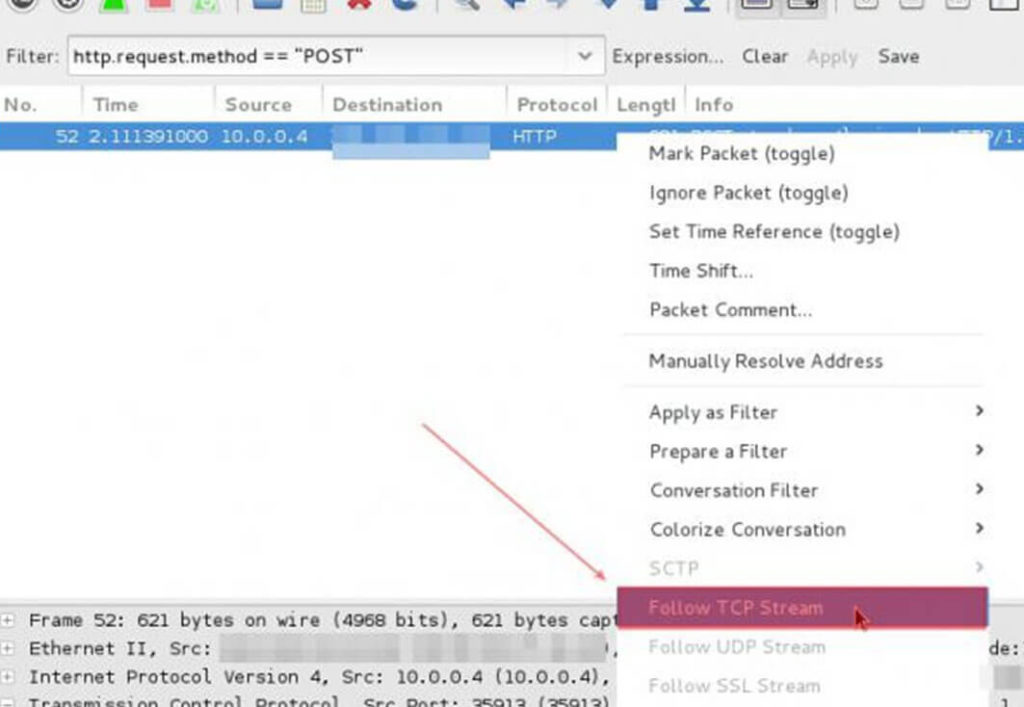
After that, a new window will display the text, which in the code restores the contents of the page. Find the fields “password” and “user”, which correspond to the password and user name. In some cases, both fields will be easily readable and not even encrypted, but if we try to capture traffic when accessing very well-known resources like Mail.ru, Facebook, Vkontakte, etc., then the password will be encoded:
HTTP / 1.1 302 Found
Date: Mon, 10 Nov 2014 23:52:21 GMT
Server: Apache / 2.2.15 (CentOS)
X-Powered-By: PHP / 5.3.3
P3P: CP = "NOI ADM DEV PSAi COM NAV OUR OTRo STP IND DEM"
Set-Cookie: non = non; expires = Thu, 07-Nov-2024 23:52:21 GMT; path = /
Set-Cookie: password = e4b7c855be6e3d4307b8d6ba4cd4ab91 ; expires = Thu, 07-Nov-2024 23:52:21 GMT; path = /
Set-Cookie: scifuser = networkguru; expires = Thu, 07-Nov-2024 23:52:21 GMT; path = /
Location: loggedin.php
Content-Length: 0
Connection: close
Content-Type: text / html; charset = UTF-8
Thus, in our case:
Username: networkguru
Password: e4b7c855be6e3d4307b8d6ba4cd4ab91
Determining the type of encoding for decrypting the password
We go, for example, to the site http://www.onlinehashcrack.com/hash-identification.php#res and enter our password into the window for identification. I was given a list of coding protocols in order of priority:
- MD5
- NTLM
- MD4
- LM
Deciphering user password
At this stage, we can use the hashcat utility:~ # hashcat -m 0 -a 0 /root/wireshark-hash.lf /root/rockyou.txtAt the output we got the decrypted password: simplepassword
Thus, using Wireshark, we can not only solve problems in the operation of applications and services, but also try ourselves as a hacker, intercepting passwords that users enter in web forms. You can also learn passwords to user mailboxes using simple filters to display:
- The POP protocol and filter looks like this: pop.request.command == “USER” || pop.request.command == “PASS”
- IMAP protocol and filter will be: imap.request contains “login”
- SMTP protocol and you will need to enter the following filter: smtp.req.command == “AUTH”
and more serious utilities to decrypt the encoding protocol.
What if the traffic is encrypted and using HTTPS?
There are several options for answering this question.Option 1: Connect to the disconnection between the user and the server and capture traffic at the time the connection is established (SSL Handshake). At the time of the connection, you can intercept the session key.
Option 2: You can decrypt HTTPS traffic using the session key log file written by Firefox or Chrome. To do this, the browser must be configured to write these encryption keys to a log file ( example based on FireFox), and you must receive this log file. In essence, it is necessary to steal a file with a session key from another user’s hard drive (which is illegal). Well, then grab traffic and use the received key to decrypt it.
Refinement. We’re talking about the web browser of the person who is trying to steal the password. If we mean decoding our own HTTPS traffic and want to practice, then this strategy will work. If you are trying to decrypt HTTPS traffic of other users without access to their computers, this will not work – for that it will encrypt and private space.
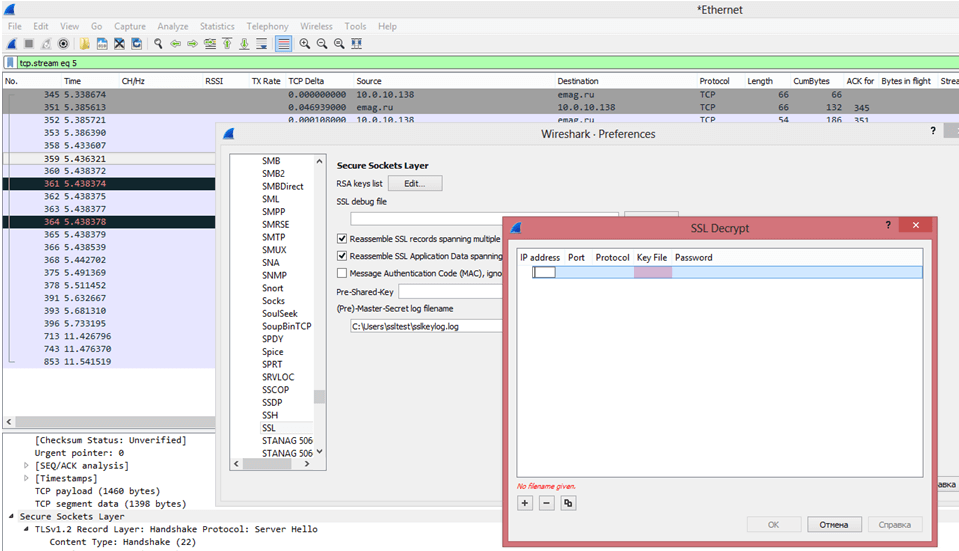
After receiving the keys for option 1 or 2, you must register them in WireShark:
- Go to the menu Edit – Preferences – Protocols – SSL.
- Set the flag “Reassemble SSL records spanning multiple TCP segments”.
- “RSA keys list” and click Edit.
- Enter data in all fields and set the path in the file with the key
WireShark can decrypt packets that are encrypted using the RSA algorithm. If the algorithms used are DHE / ECDHE, FS, ECC, the sniffer is not our helper.
Option 3. Get access to the web-server, which the user uses, and get the key. But it is even more challenging. In corporate networks for the purpose of debugging applications or content filtering, this option is implemented on a legal basis, but not in order to intercept user passwords.

Leave a Reply