How to use rkhunter to Scan for Rootkits, backdoors and Exploits Using in Linux
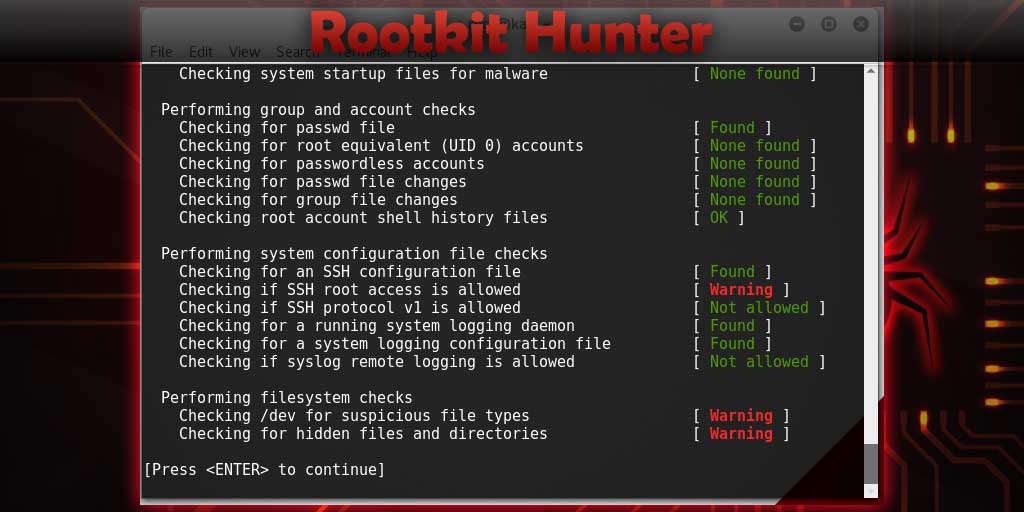
Rkhunter “Rootkit Hunter”. it can find about 58 known rootkits and some sniffer and backdoor programs. It performs a series of test scripts to confirm whether the server has been infected with rootkits, such as checking the basic files used by rootkits, wrong file permissions for executable binaries, detecting kernel modules, and so on. In official information, RKHunter can do:
- the MD5 checksum test, detects whether there are changes file
- binary files and system tools used for detecting rootkit
- signature detection Trojan
- the detection procedure used is abnormal file attributes
- the detection system associated test
- Detect hidden files
- Detect suspicious core module LKM
- Detect the monitoring port that the system has started
After completing the above tests, your screen will display the scan results: files that may be infected, incorrect MD5 checksums The infected application.
What Is Rkhunter?
Rkhunter (Rootkit Hunter) is an open source Unix/Linux based scanner tool for Linux systems released under GPL that scans backdoors, rootkits and local exploits on your systems.
It scans hidden files, wrong permissions set on binaries, suspicious strings in kernel backdoors and possible local exploits. It does this by comparing SHA-1 hashes of important files with known good ones in online databases.
What is rootkit
The rootkit is the most common Trojan backdoor tool under the Linux platform. It mainly achieves the purpose of intrusion and concealment by replacing system files. This Trojan is more dangerous and concealed than ordinary Trojan backdoors. It is difficult for ordinary detection tools and inspection methods Found this Trojan.
The rootkit is extremely capable of attack and is very harmful to the system. It uses a set of tools to create backdoors and hide trails, so that the attacker can retain permissions so that it can log in to the system with root permissions at any time.
There are two main types of rootkits : file level and kernel level.
file level rootkit
File-level rootkits: Generally, after entering the system through program vulnerabilities or system vulnerabilities, the important files of the system are modified to hide themselves. After the system was attacked by rootkit, the legitimate files were replaced by Trojan horse programs and turned into shell programs, and the hidden backdoor programs were inside.
System programs that are usually easily replaced by rootkits include login, ls, ps, ifconfig, du, find, netstat, etc. File-level rootkits are very harmful to the system. At present, the most effective defense method is to regularly check the integrity of important system files, such as Tripwire and aide.
Kernel level rootkit
Kernel-level rootkit: It is a more advanced way of intrusion than file-level rootkit. It can enable an attacker to gain complete control over the bottom layer of the system. At this time, the attacker can modify the system kernel to intercept the commands submitted by the running program to the kernel. And redirect it to the program selected by the intruder and run this program.
The kernel-level rootkit is mainly attached to the kernel, it does not make any modifications to the system files. Focus on prevention. Generally, the system image should be downloaded from the official website or a website with high credibility.
How to install rkhunter
Install Rootkit Hunter Scanner in Linux
If you are running Kali Linux you can install it by this terminal command
sudo apt-get install rkhunter
To install rkhunter on Fedora execute the following command:
sudo dnf install rkhunter-1.4.2-11.fc24.noarch
if you are not using kali linux Download Rkhunter by this terminal command
wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/rkhunter/rkhunter/1.4.2/rkhunter-1.4.2.tar.gz
Once you have downloaded Rkhunter, run the following commands as a root user
tar -xvf rkhunter-1.4.2.tar.gz
cd rkhunter-1.4.2
./installer.sh --layout default --install
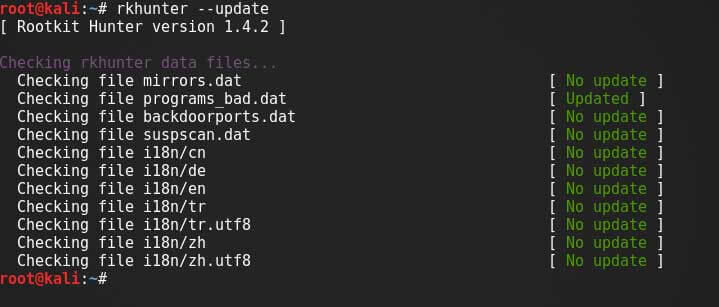
To update Rkhunter
rkhunter --update
How to use rkhunter
you can check whether your machine has been infected with a rootkit by running the following command:
rkhunter -c
By default, rkhunter performs some known tests on the system. But you can also perform it by using ‘–scan-knownbad-files’ unknown error detection:
rkhunter -c -scan-knownbad-Files
rkhunter is detected by a name containing the rootkit rootkits vulnerabilities database system, the database is updated frequently so it’s very important to keep updating your database

Leave a Reply