
lsblk:
lsblk command allows you to display a list of available block devices.
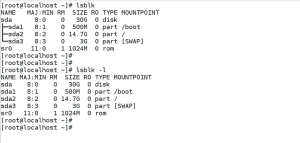
lsblk command displays the device name (NAME), major and minor device number (MAJ:MIN), if the device is removable (RM), what is its size (SIZE), if the device is read-only (RO), what type is it (T YPE), and where the device is mounted (MOUNT POINT ). Reember, by default lsblk command shows ouput in tree format. To display the information as an ordinary list, add the -l command line option.
blkid
blkid command, as was under RHEL6, in RHEL7 is used to view information about available block devices.
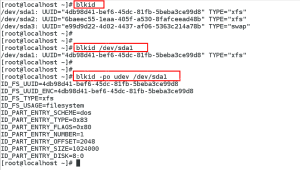
Be default, the blkid command displays available attributes such as its universally unique identifier (UUID), file system type (T YPE), or volume label (LABEL), as in command one, in above snapshot.
You can also use blkid to display information about a particular device only, specify the device name on the command line – blkid /dev/sda1, as in command two, above snapshot.
Further, you can also use the above command with the -p and -o udev command line options to obtain more detailed information. You need to have root privileges to run the third command in above snapshot.
findmnt
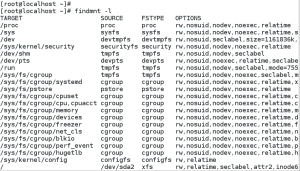
findmnt command allows you to display a list of currently mounted file systems. findmnt command displays the target mount point (TARGET ), source device (SOURCE), file system type (FSTYPE), and relevant mount options (OPT IONS).
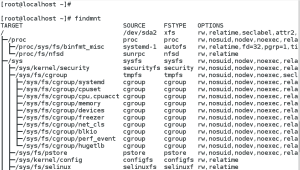
Like lsblk command, findmnt lists file systems in a tree-like format. T o display the information as an ordinary list, add the -l command line option.
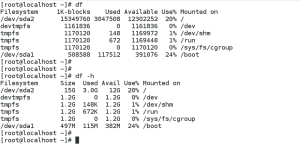
df
Exactly like in RHEL6, here in RHEL7 df command allows you to display a detailed report on the system’s disk space usage. df command displays its name (Filesystem ), size (1K-blocks or Size), how much space is used (Used), how much space is still available (Available), the percentage of space usage (Use%), and where is the file system mounted (Mounted on).
Similar like in RHEL6, the df command in RHEL7 shows the partition size in 1 kilobyte blocks and the amount of used and available disk space in kilobytes. To view the information in megabytes and gigabytes, supply the -h command line option, human-readable format.
du
du command allows you to displays the amount of space that is being used by files in a directory. Like df, du command displays the disk usage in kilobytes. T o view the information in megabytes and gigabytes, supply the -h command line option and to get the summary information only use -s option.

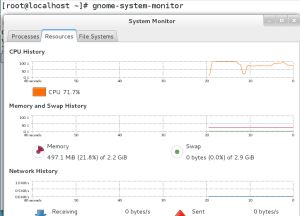
And lastly, you have the gnome-system-monitor tool in rhel7 viewing block devices & filesystem.

Leave a Reply